If you are considering retiring early and would like to use your pre-tax retirement accounts before age 59½ then you have significant planning to ensure you make the most of your retirement assets. One possibility is to use a 72(t) exception to avoid the early withdrawal penalty from pre-tax accounts. This 10% penalty is in addition to ordinary income tax.
An exception to the 10% penalty is the 72(t)(2)(A)(iv) OR “a series of substantially equal periodic payments (not less frequently than annually) made for the life (or life expectancy) of the employee or the joint lives (or joint life expectancies) of such employee and his designated beneficiary”. This exception allows for regular payments from pre-tax accounts but must be tailored to your specific situation.
In general, the 72(t) exception requires that a calculated payment be withdrawn from a pre-tax account annually for the longer of five years or at age 59½. The advantage is that the 10% penalty can be avoided but the disadvantage is that changes to withdrawals or distributions are NOT permitted, or penalties apply. When calculating the annual payment, we consider the age of the pre-tax account owner, the balance in the pre-tax account, and the current interest rate. Higher payments are obtained at later ages, with higher account balances and at higher interest rates.
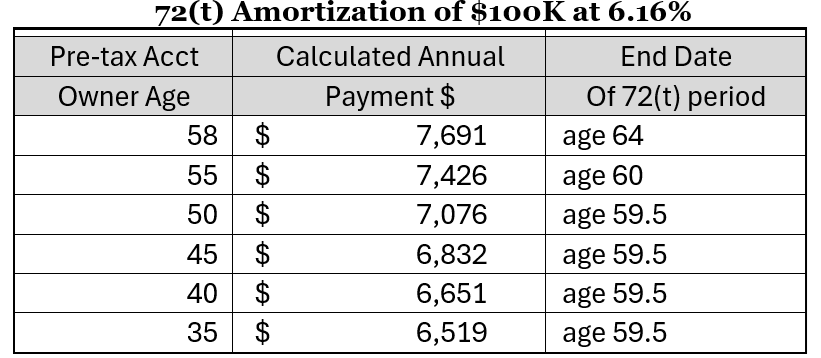
To help you visualize how the 72(t) amortization works, the table below shows annual payments for a single person at different ages on an account with $100K in pre-tax savings given that the current interest rate is at 6.16%.
Those thinking to retire early should consider using pre-tax assets (with the 72(t) exception) to support their planned cash flow but only if it is the best way to deploy all available assets. When using the 72(t)-exception you need to understand the implications of the rules since large penalties apply for errors or misunderstandings. If you are considering retiring early, we would determine how to best deploy your assets throughout your retirement plan.
Edi Alvarez, CFP®
BS, BEd, MS